mojo's Blog
인접 행렬을 이용한 다익스트라 구현 본문
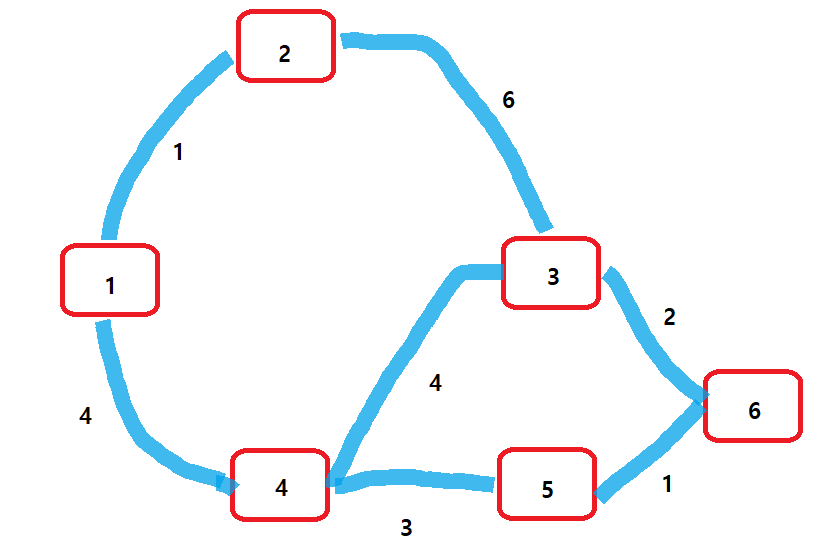
인접 행렬을 이용한 다익스트라 알고리즘을 구현한 코드이다.
Solution Code
c++
닫기/* Dijkstra's algorithm for a digraph in adjacency matrix */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void create_graph(void);
void display(void);
int find_path(int, int, int*, int*);
#define MAX 4096
#define TEMP 0
#define PERM 1
struct node {
int predecessor;
int dist; /*minimum distance of node from source*/
int status;
};
int n, adj[MAX][MAX];
void main() {
int i, source, dest;
int path[MAX];
int shortdist, count;
// Adjacent Matrix 을 만드는 함수 호출
create_graph();
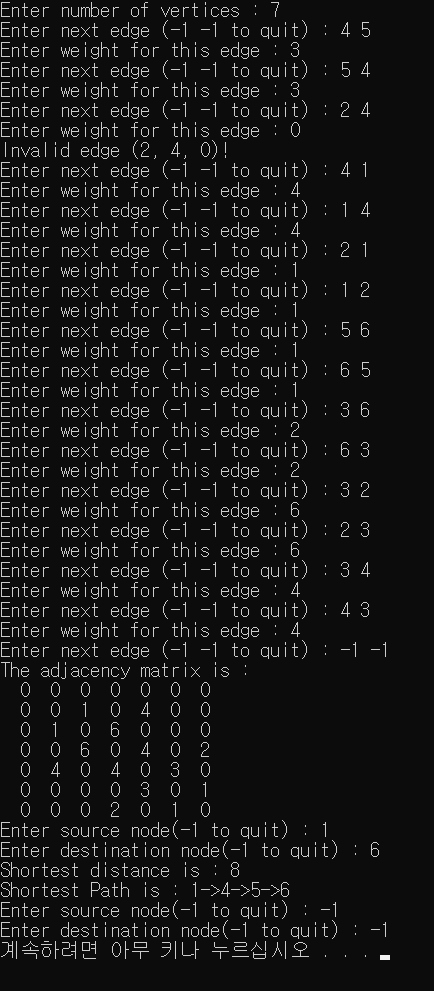
printf("The adjacency matrix is :\n");
display();
while (1) {
printf("Enter source node(-1 to quit) : ");
scanf("%d", &source);
printf("Enter destination node(-1 to quit) : ");
scanf("%d", &dest);
if (source == -1 || dest == -1) exit(1);
count = find_path(source, dest, path, &shortdist);
if (shortdist != 0) { // source ~> dest 로 가는 최단 경로를 찾음
printf("Shortest distance is : %d\n", shortdist);
printf("Shortest Path is : ");
for (i = count; i > 0; i--)
printf("%d->", path[i]);
printf("%d", path[0]);
printf("\n");
}
else // 0일 경우 source ~> dest 로 가는 경로가 존재하지 않음!
printf("There is no path from source to destination node\n");
}
}
void create_graph(void) {
int origin, destin, wt;
printf("Enter number of vertices : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Adjacent Matrix 의 초기화 작업
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
adj[i][j] = 0;
// origin ~> destin 의 거리 wt 에 대한 Adjacent Matrix 의 세팅과정
while (1) {
printf("Enter next edge (-1 -1 to quit) : ");
scanf("%d %d", &origin, &destin);
if ((origin == -1) && (destin == -1))
break;
printf("Enter weight for this edge : ");
scanf("%d", &wt);
if (origin >= n || destin >= n || origin < 0 || destin < 0 || wt <= 0) {
printf("Invalid edge (%d, %d, %d)!\n", origin, destin, wt);
}
else adj[origin][destin] = wt;
}
}
void display(void) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
printf("%3d", adj[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
// Dijkstra algorithm 을 Adjacent Matrix으로 구현한 코드
int find_path(int s, int d, int path[MAX], int* sdist) {
struct node state[MAX];
int i, min, current, newdist, u, v;
/* Make all nodes temporary */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
state[i].predecessor = -1; // i번째 노드의 자손을 -1으로 (경로 추적을 위한 용도로 쓰임)
state[i].dist = INT_MAX; // s번째 노드에서 i번째 노드로 갈 수 있는 최단 거리
state[i].status = TEMP; // i번째 노드를 방문했는지에 대한 확인용도
}
/* Source node should be permanent */
state[s].predecessor = s; // 자기 자신을 자손으로 설정하며
state[s].dist = 0; // 자기 자신으로 가는 경로의 길이는 당연히 0이고
state[s].status = PERM; // 자기 자신을 방문했으므로 체크
/* Starting from source node until destination is found */
current = s; // 현재 위치에 대한 변수
while (current != d) { // 목적지에 도착할 때까지 반복
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
/* Checks for adjacent temporary nodes */
// current ~> i 로 가는 경로가 존재하며 i번째 노드를 방문하지 않은 경우
if (adj[current][i] > 0 && state[i].status == TEMP) {
newdist = state[current].dist + adj[current][i];
/* Checks for Relabeling */
if (newdist < state[i].dist) { // current ~> i 로 가는 경로가 기존에 i로 가는 경로에 비해 짧을 경우
state[i].predecessor = current; // i번째 자손을 current 으로 설정
state[i].dist = newdist; // 거리가 더 짧은 걸로 변경해준다.
}
}
}
/* Search for temporary node with minimum distand make it current node */
min = INT_MAX; current = -1;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// i번째 노드로 가는 경로중에 가장 최소가 되는 노드를 선별한다.
if (state[i].status == TEMP && state[i].dist < min) {
min = state[i].dist;
current = i;
}
}
// 선별할 수 없을 경우 고립된 경우로 0을 반환함
if (current == -1) /* If Source or Sink node is isolated */
return 0;
// current 로 가는 경로가 가장 최소가 되는 경우가 된 경우이므로 방문 처리를 함
state[current].status = PERM;
} /*End of while*/
/* Getting full path in array from destination to source */
int count = 0;
path[count] = current;
// path 배열에 dest 에서 source 로 역으로 경로를 담아주는 모습이다.
while (state[current].predecessor != current) {
current = state[current].predecessor;
path[++count] = current;
}
/* Getting distance from source to destination */
// 역으로 담았던 path 배열을 통해 최단 거리의 길이를 반환하도록 한다.
*sdist = 0;
for (i = count; i > 0; i--) {
u = path[i]; v = path[i - 1];
*sdist += adj[u][v];
}
return count;
}
'학교에서 들은거 정리 > 알고리즘설계와분석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Prim's Algorithm, Dijkstra's Algorithm (0) | 2021.12.09 |
|---|---|
| Scheduling with Deadlines with Disjoint Sets (0) | 2021.12.07 |
| Disjoint Sets (0) | 2021.11.30 |
| Scheduling with Deadlines (0) | 2021.11.25 |
| Scheduling (0) | 2021.11.23 |




