mojo's Blog
Scheduling with Deadlines 본문
Problem
– Let J = {1, 2, …, n} be a set of jobs to be served.
– Each job takes one unit of time to finish.
– Each job has a deadline and a profit.
• If the job starts before or at its deadline, the profit is obtained.
➢ Schedule the jobs so as to maximize the total profit (not all jobs have to be scheduled).
예를 들어서 다음과 같은 Job(Deadline, Profit)이 4개 존재한다고 하자
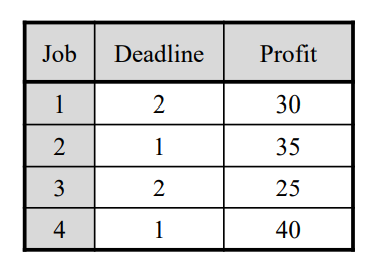
이때, 최대 이익을 낼 수 있는 경우는 job = [4, 1] 인 경우 total = 75 인 경우다.
또 다른 예를 살펴보도록 하자.
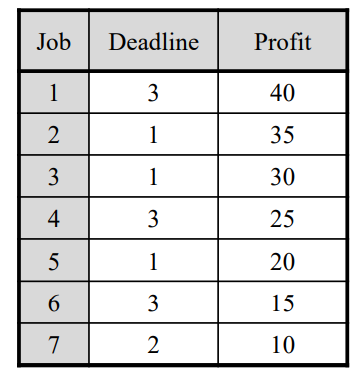
이 경우는 job = [1, 2, 4] 와 같이 잡을 수 있다.
즉 Greedy 접근법으로
(1) profit 을 기준으로 내림차순으로 job들을 정렬하고 => O(nlogn)
(2) 정렬된 각 job에 대한 Scan을 함으로써 schedule 가능한 경우에 대해서 추가하는 방식이다.
linked-list로 구현할 경우 O(n^2), disjoint set으로 구현할 경우 O(nlogn)
위 예시로 다시 구해보면 ...
0. S = EMPTY
1.S = {1} ? => 가능
2. S = {1, 2} ? => 가능
3. S = {1, 2, 3} ? => 불가능
4. S = {1, 2, 4} ? => 가능

Linked-List 로 구하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
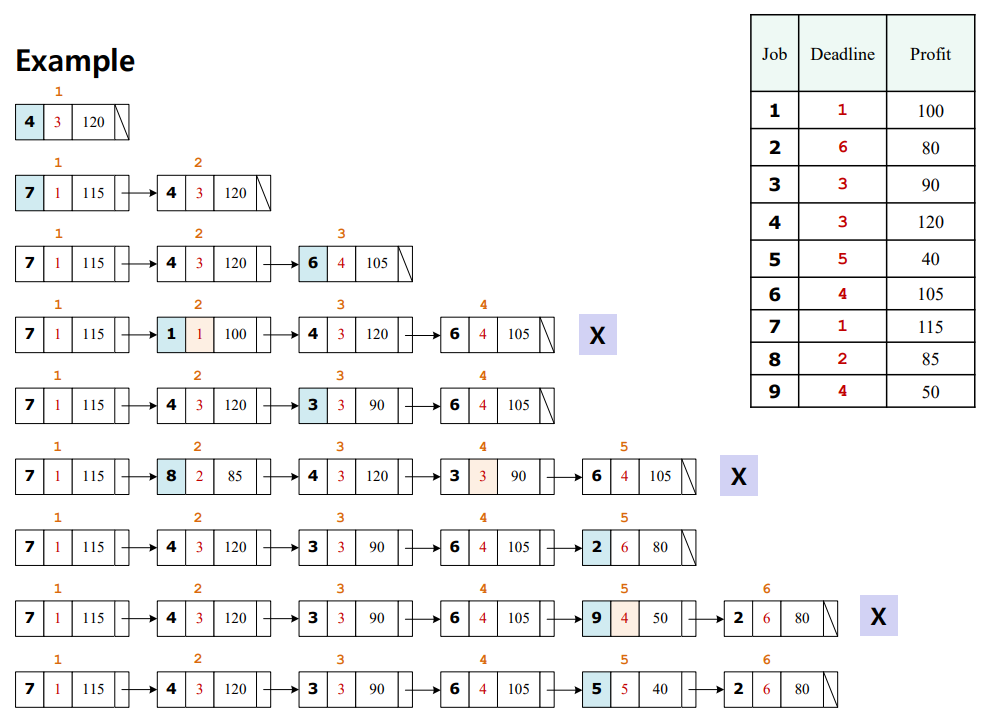
Solution Code
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
struct Job {
int job;
int Deadline;
int Profit;
};
struct Node {
int job;
int Deadline;
int Profit;
struct Node* next, * prev;
};
Job job[100];
Node* root, root_dummy, dummy[100];
int deadline[9] = { 1,6,3,3,5,4,1,2,4 };
int profit[9] = { 100,80,90,120,40,105,115,85,50 };
int max_deadline = 6, job_cnt, mem_pool;
bool visited[100];
void Print_all_node()
{
Node* tmp;
tmp = root;
while (tmp->next) {
tmp = tmp->next;
printf("[%d, %d, %d] / ", tmp->job, tmp->Deadline, tmp->Profit);
}
}
void set_node()
{
root_dummy.next = root_dummy.prev = nullptr;
root = &root_dummy;
}
Node* get_node(Job tmp)
{
dummy[mem_pool].Deadline = tmp.Deadline;
dummy[mem_pool].job = tmp.job;
dummy[mem_pool].Profit = tmp.Profit;
return &dummy[mem_pool++];
}
void Node_insert(Job tmp)
{
int cnt = 1;
Node* new_node;
if (mem_pool == max_deadline)
return;
if (root->next == nullptr) {
new_node = get_node(tmp);
root->next = new_node;
new_node->prev = root;
visited[tmp.Deadline] = true;
}
else {
Node* node_tmp = root;
while (node_tmp->next) {
node_tmp = node_tmp->next;
if (node_tmp->Deadline > tmp.Deadline)
break;
cnt++;
}
if (cnt > tmp.Deadline)
return;
int x = tmp.Deadline;
while (visited[x]) x--;
if (x == 0)
return;
visited[x] = true;
new_node = get_node(tmp);
if (cnt == mem_pool) {
node_tmp->next = new_node;
new_node->prev = node_tmp;
}
else {
node_tmp->prev->next = new_node;
new_node->next = node_tmp;
new_node->prev = node_tmp->prev;
node_tmp->prev = new_node;
}
}
}
void PQ_insert(int n, int d, int p)
{
int x;
x = ++job_cnt;
while ((x != 1) && (job[x / 2].Profit < p)) {
job[x] = job[x / 2];
x /= 2;
}
job[x].job = n, job[x].Deadline = d, job[x].Profit = p;
}
Job PQ_pop()
{
int parent, child;
Job item, temp;
item = job[1], temp = job[job_cnt--];
parent = 1, child = 2;
while (child <= job_cnt) {
if ((child < job_cnt) && (job[child].Profit < job[child + 1].Profit)) child++;
if (temp.Profit >= job[child].Profit) break;
job[parent] = job[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
job[parent] = temp;
return item;
}
void Scheduling()
{
int i, before;
Job tmp;
for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
PQ_insert(i + 1, deadline[i], profit[i]);
}
set_node();
for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
printf("%d : ", i + 1);
before = mem_pool;
tmp = PQ_pop();
Node_insert(tmp);
Print_all_node();
if (before == mem_pool)
printf("X\n\n");
else
printf("O\n\n");
}
}
int main()
{
Scheduling();
return 0;
}

'학교에서 들은거 정리 > 알고리즘설계와분석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Scheduling with Deadlines with Disjoint Sets (0) | 2021.12.07 |
|---|---|
| Disjoint Sets (0) | 2021.11.30 |
| Scheduling (0) | 2021.11.23 |
| Huffman Coding (0) | 2021.11.16 |
| Subset Sum Problem (0) | 2021.11.09 |




