mojo's Blog
Huffman Coding 본문
0-1 Knapsack Example 2: n = 6, W = 10
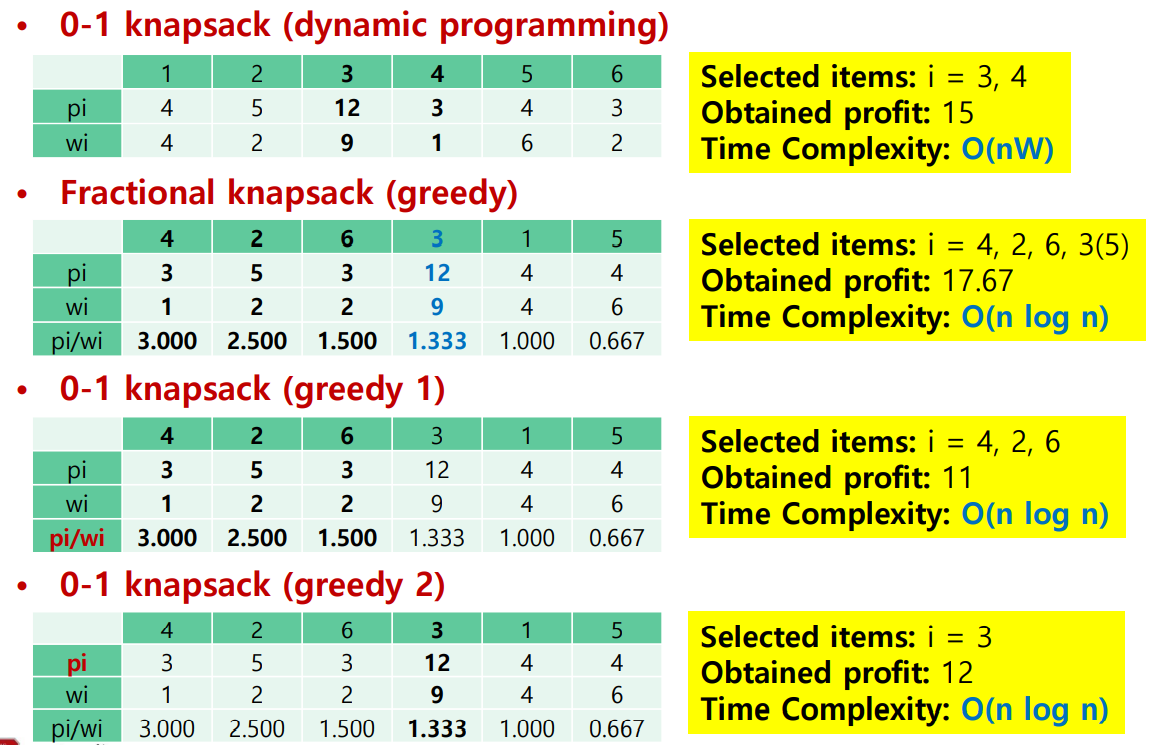
알고리즘 별로 획득되는 이익이 다른것을 알 수 있다.
위 예제에서 그나마 좋은 알고리즘이 greedy 알고리즘인데 이 중에 최대 이익을 뽑아낼 수 있는 알고리즘을
활용하여 O(nlogn) 의 효율을 뽑아서 이익을 뽑도록 한다.
The Greedy Methods
A technique to follow the problem-solving heuristic of making the locally optimal choice at each stage.
※ Strategy
- 매 순간마다 가장 최선인 것을 선택하는 방법이다.
- 즉, locally optimal를 선택함으로써 globally optimal을 도달하려는 것이 궁극적인 목표이다.
※ Pros and cons
- 알고리즘을 simple, straightforward 하게 설계한다.
- 그러나 모든 문제에 대한 optimal solution을 보장하지 못한다는 점이 있다.
Huffman Coding
※ Data compression
- Data compression can save storage space for files.
- Huffman coding is just one of many data compression techniques.
※ Problem
- 파일이 주어질 때, file 안에 담긴 character들에 대한 binary character code를 발견하는 것이다.
- 그것도 가장 적은 bit 들로 표현이 가능해야 한다.
예시를 살펴보도록 하자.
원래의 텍스트 파일 "ababcbbbc" 가 있다고 해보자.
Huffman code 로 a = 10, b = 0, c = 11 이 주어졌다고 할 때, 다음과 같이 encoding 가능하다.
Compressed file : 1001001100011
Prefix Codes
Huffman code 로 encoding을 하고 그 다음에 유일하게 decoding 이 가능해야 의미가 있다.
다음 예제를 살펴보도록 한다.
Example 1 : a = 00, b = 1110, c = 110, ...
111000110... 가 존재한다고 할 때, 보통 character를 왼쪽에서부터 접근하는 방법을 이용한다.
즉, 111000110... 과 같이 decoding 하면 bac... 와 같이 된다.
Example 2 : a = 00, b = 1100, c = 110, ...
1100000... 가 존재한다고 할 때, conflict가 발생하는 것으로 보인다.
맨 처음에 11 다음에 1100 으로 잡아서 b라고 할지, 110 으로 잡아서 c라고 할지에 대한 conflict가 발생한다.
※ Binary trees corresponding to prefix codes
- The code of a character c is the label of the path from the root to c.
- Decoding of an encoded file is trivial.
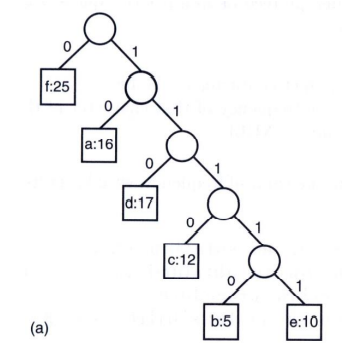
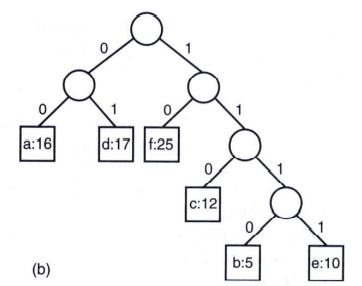
※ Problem
- character set V = {v1, v2, ..., vn} 으로 인코딩된 주어진 file 에 대해서 다음과 같은 cost function을 최소화하는
binary tree T으로 구성된 optimal prefix binary code를 찾아야 한다.
cost function은 다음과 같다.
bits(T) = freq(v1) * depth(v1) + ... + freq(vn) * depth(vn)
freq(vi) : 해당 문자 vi가 file에서 나타난 빈도수를 의미한다.
depth(vi) : 해당 문자 vi의 tree T의 깊이를 의미한다.
A Greedy approach successfully finds an optimal code.
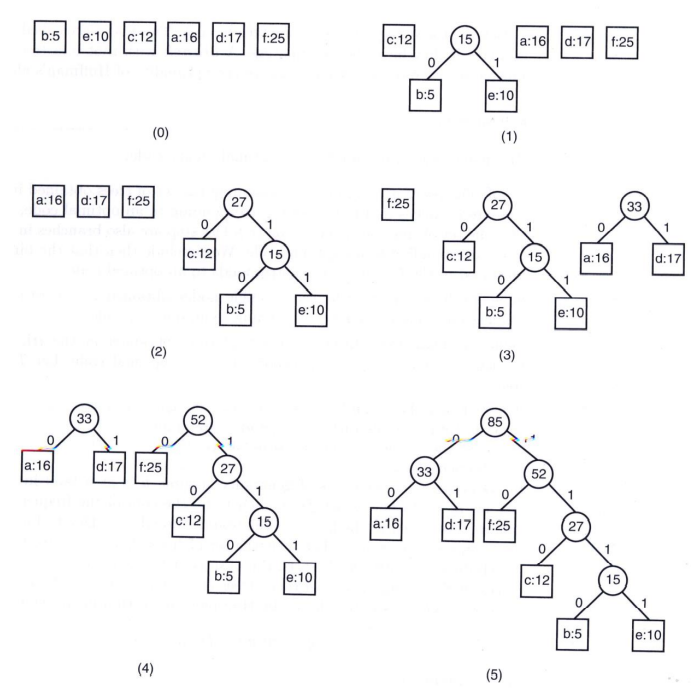
Huffman's Algorithm
※ A greedy approach
- Repeat the following until only one tree is left:
① Start from a set of single node trees
② Pick up two trees u and v with the lowest frequencies (min heap 이용)
③ Merge them by adding a root node w wheree the frequency of the new node is
the sum of those of u and v.
④ Replace u and v by w.
Solution Code
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct _node {
char symbol;
int freq;
struct _node* left;
struct _node* right;
} NODE;
NODE* u, * v, * w;
NODE* node[7];
char symbolSet[7] = { '_','b','e','c','a','d','f' };
int freqSet[7] = { -1,5,10,12,16,17,25 };
int n = 6, node_cnt, total_freq;
void PQ_insert(NODE* tmp)
{
int x;
x = ++node_cnt;
while ((x != 1) && (tmp->freq < node[x / 2]->freq)) {
node[x] = node[x / 2];
x /= 2;
}
node[x] = tmp;
}
NODE* PQ_delete()
{
int parent, child;
NODE *item, *temp;
item = node[1], temp = node[node_cnt--];
parent = 1, child = 2;
while (child <= node_cnt) {
if ((child < node_cnt) && (node[child]->freq > node[child + 1]->freq)) child++;
if (temp->freq <= node[child]->freq) break;
node[parent] = node[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
node[parent] = temp;
return item;
}
NODE* make_a_new_node()
{
return (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
}
void Set_Single_Node(char s, int f)
{
int x;
NODE* tmp;
tmp = make_a_new_node();
tmp->symbol = s;
tmp->freq = f;
tmp->left = tmp->right = nullptr;
PQ_insert(tmp);
}
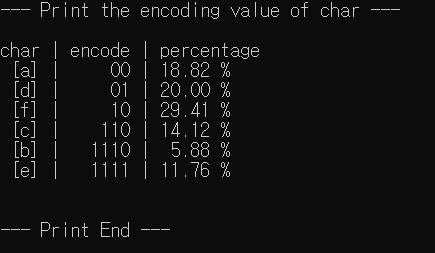
void Print_Tree(NODE* tmp, int depth, char *encoding) {
if (tmp) {
encoding[depth] = '0';
Print_Tree(tmp->left, depth + 1, encoding);
if (tmp->left == nullptr && tmp->right == nullptr) {
encoding[depth] = '\0';
printf(" [%c] | %6s | %5.2f %%\n", tmp->symbol, encoding,
((float)tmp->freq / (float)total_freq) * (float)100);
}
encoding[depth] = '1';
Print_Tree(tmp->right, depth + 1, encoding);
}
}
void Find_Depth(NODE* tmp, int depth, int& max_depth)
{
if (tmp) {
Find_Depth(tmp->left, depth + 1, max_depth);
if (tmp->left == nullptr && tmp->right == nullptr)
max_depth = max_depth < depth ? depth : max_depth;
Find_Depth(tmp->right, depth + 1, max_depth);
}
}
void Huffman_Coding()
{
int i, tree_depth;
char* encoding;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Set_Single_Node(symbolSet[i], freqSet[i]);
total_freq += freqSet[i];
}
for (i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++) {
u = PQ_delete();
v = PQ_delete();
w = make_a_new_node();
w->left = u;
w->right = v;
w->freq = u->freq + v->freq;
PQ_insert(w);
}
w = PQ_delete();
/* w points to the optimal tree. */
/* find the maximum of tree depth. */
tree_depth = 0;
Find_Depth(w, 0, tree_depth);
/* Print the encoding value of char */
encoding = (char *)malloc((tree_depth + 1));
printf("--- Print the encoding value of char ---\n\n");
printf("char | encode | percentage \n");
Print_Tree(w, 0, encoding);
printf("\n\n--- Print End ---\n\n");
}
int main()
{
Huffman_Coding();
return 0;
}
'학교에서 들은거 정리 > 알고리즘설계와분석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Scheduling with Deadlines with Disjoint Sets (0) | 2021.12.07 |
|---|---|
| Disjoint Sets (0) | 2021.11.30 |
| Scheduling with Deadlines (0) | 2021.11.25 |
| Scheduling (0) | 2021.11.23 |
| Subset Sum Problem (0) | 2021.11.09 |




